Post By
Gateway Diagnostic Imaging
Date
July 25, 2024
Can a CT scan show brain tumors?
When your healthcare provider wants to know whether you have a brain tumor, they may recommend a CT scan, which can give them very clear images of your brain tissue.
You might feel a little worried or anxious about what your CT results might say, but you can rest assured that a brain CT scan is a trustworthy scan for finding brain tumors, and making a treatment plan to support your care.
In this guide, we’ll find out what a brain CT does, learn how a CT scan finds potential tumors, and what you can expect before, during, and after your brain CT scan.
What is a brain CT scan? How does a brain CT scan work?
A brain CT scan, also known as a computed tomography scan, is a detailed imaging technique used to create clear and precise pictures of the brain. The process involves lying on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine.
This machine takes a series of X-ray images from different angles around your head. A computer then processes these images to create cross-sectional views, or slices, of your brain. These slices provide detailed information, allowing healthcare providers to see the brain’s structure in great detail.
The entire scan is non-invasive and usually takes only a few minutes. During the scan, you will need to lie still, but the process is generally quick and painless. The images produced can help identify various conditions, including tumors, by highlighting differences in tissue density.
Why did my healthcare provider recommend a brain CT scan for detecting a potential brain tumor?
Your healthcare provider may recommend a brain CT scan if you are experiencing symptoms that could indicate a brain tumor, such as persistent headaches, changes in vision, unexplained nausea, or neurological changes like weakness or speech difficulties.
A brain CT scan is a reliable and effective method to detect the presence of brain tumors because it provides clear images of the brain’s structure. These images can reveal abnormal growths, masses, or changes in tissue density that may suggest a tumor.
A brain CT scan can also help differentiate between different types of brain tumors, such as benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) tumors. The detailed images help healthcare providers determine the size, location, and characteristics of a tumor, which is crucial for planning further diagnostic tests or treatments.
How a CT scan detects brain tumors
Now that you know how a brain CT works, let’s find out how a CT scan can find a potential brain tumor, and how a brain CT compares to a scan like a brain MRI for diagnosing a possible tumor. We want to help you understand why your provider ordered a brain CT scan rather than another kind of diagnostic imaging, like an MRI.
How does a brain CT scan create images of a brain tumor?
A brain CT scan uses advanced imaging technology to produce detailed pictures of the brain. The images produced by a CT scan can show various types of brain tissue, including bone, soft tissues, and any unusual growths like tumors.
The technology is designed to highlight differences in tissue density, which helps in identifying abnormal areas that could indicate a tumor. By producing clear, detailed images, a brain CT scan allows healthcare providers to see the exact size, location, and shape of any potential tumors.
What are the typical features of brain tumors visible on a CT scan?
Brain tumors often appear as distinct areas that differ in density from the surrounding brain tissue. On a CT scan, these tumors may look like a mass or a growth that stands out against the normal background of the brain.
The tumors can vary in appearance based on their type and composition. For instance, some tumors may appear as solid, well-defined masses, while others might have irregular borders or be surrounded by swelling.
How do radiologists interpret CT scan images for brain tumors?
Radiologists are medical professionals specialized in interpreting imaging studies, including CT scans. When they examine a brain CT scan, they look for any abnormal areas that could indicate the presence of a tumor.
They assess the size, shape, and location of any suspicious masses, and compare these features to the normal anatomy of the brain. Radiologists also look for other signs that might suggest a tumor, such as swelling or changes in the surrounding brain tissue.
After carefully analyzing the images, the radiologist provides a detailed report to your healthcare provider. This report includes their findings and an interpretation of what the images suggest. The information in the report helps your healthcare provider understand whether a tumor is present.
How do CT scans compare to other imaging techniques for detecting brain tumors?
CT scans are often compared to MRI scans when it comes to detecting brain tumors. While CT scans are excellent for quickly identifying large tumors and providing detailed images of bone structures, MRIs are typically better at differentiating between soft tissues. This means that MRIs can often provide more detailed images of the brain’s internal structures and detect smaller or more complex tumors.
However, CT scans are usually faster and more readily available, making them a good first step in many diagnostic processes. In some cases, a healthcare provider might recommend both a CT scan and an MRI to get a comprehensive view of the brain. Each imaging technique has its strengths, and the choice of which to use will depend on the specific details of your care.
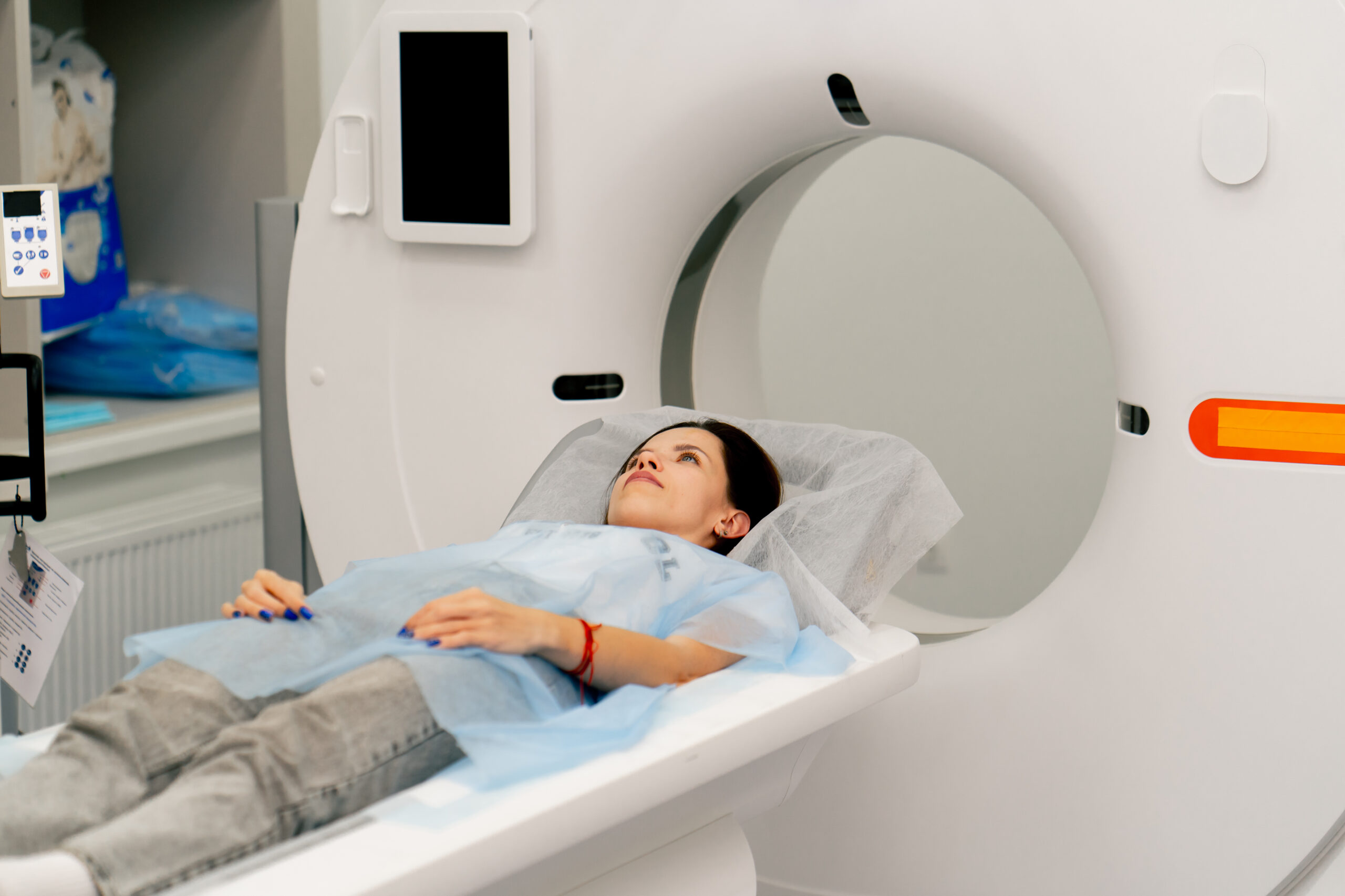
What to expect during your brain CT scan for brain tumors
You may or may not have had a CT scan before, but if you’ve never had a brain CT before, you should know that a brain CT is a quick and painless scan that requires minimal prep. Let’s look at how to get ready for a brain CT, what happens during the scan, and how long it takes.
How should I prepare for a brain CT scan?
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions, but generally, you can eat and drink as usual unless instructed otherwise. You might need to remove any jewelry, glasses, or metal objects that could interfere with the imaging process. It’s also a good idea to wear comfortable clothing that you can easily change out of if necessary.
If your scan requires the use of contrast dye (see below), which provides more detailed information about your brain, you may be asked to fast for a few hours before the scan. Make sure to inform your healthcare provider about any allergies or previous reactions to contrast dye, as well as any current medications or medical conditions.
What happens during a CT scan for brain tumors?
After you check in for your brain CT scan, you will be guided to the scanning area, and asked to lie down on a cushioned table. The technologist will position you comfortably, and may use pillows or straps to help you stay still during the scan. The table will then slowly move into the circular scanning machine, which surrounds your head.
The machine takes a series of images as it rotates around your head, capturing detailed pictures from various angles. You will need to remain as still as possible to ensure the images are clear and accurate. Your technologist will be in a separate room monitoring the scan, but they can see you, and communicate with you throughout the process. You might hear some whirring or clicking sounds from the machine, but the scan itself is painless.
What is contrast dye, and why would I need it during a CT scan for brain tumors?
Contrast dye is a special substance used during some CT scans to improve the clarity of the images. It is typically administered through an intravenous (IV) line, and it helps highlight certain areas of your brain by making them appear brighter on the scan. This enhanced visibility can be particularly useful in detecting and characterizing brain tumors.
Using contrast dye allows radiologists to see more detailed information about the structure and blood vessels within your brain, and it can help identify tumors more accurately. Not everyone needs contrast dye for a brain CT scan, so your healthcare provider will decide if it is necessary based on your specific situation. If you have any concerns about the contrast dye, be sure to discuss them with your healthcare provider before your CT scan.
How long does a brain CT scan take?
A brain CT scan is relatively quick and typically takes about 10 to 30 minutes to complete. The actual scanning process is usually only a few minutes long, but the additional time allows for preparation and positioning. If contrast dye is used, the scan may take a bit longer, to administer the dye and to allow it to circulate through your bloodstream.
After the scan, you can generally resume your normal activities immediately. Your healthcare provider will let you know if there are any specific post-scan instructions to follow. A radiologist will review your results, and then provide a detailed report to your healthcare provider.
How to schedule your CT with us
When you get your scan at one of our imaging centers, we’ll make sure you have access to affordable, high-quality medical imaging from specialized radiologists and certified technologists.
Reach out to a Gateway imaging center near you, and schedule your appointment today.
